Unggulan
- Dapatkan link
- X
- Aplikasi Lainnya
Ideal Gas Law R Values / Ideal gas law practice mccpot / Apply the ideal gas law to solve problems in chemistry.
Ideal Gas Law R Values / Ideal gas law practice mccpot / Apply the ideal gas law to solve problems in chemistry.. Ideal gas law calculations pv=nrt tutorial with worked examples for chemistry students. Values of r (gas constant). It's very simple, easy to use, and easy to understand. The law of ideal gases states that the volume of a specified amount of gas is inversely proportional to pressure and directly proportional to volume and now if the physical conditions of temperature, pressure and volume show variation then the initial values shall be t1, p1 and v1 while the final. One mole of any gas at standard temperature and pressure (stp) occupies a standard volume of 22.4 liters.
The ideal gas law states that p x v = n x r x t where, p is pressure, v is volume, n is number of moles of the gas, r is the ideal gas constant and t is temperature in kelvin. The kinetic theory of gases. It is a combination of the previous laws that we have studied (boyle's, charles', avogadro's). Ideal gas laws are used to find the species partial pressures and hence cathode exit pressure the ideal gas laws work well at relatively low pressures and relatively high temperatures. It's always the same for all calculations you perform by choosing one of those whose unit fits the question.
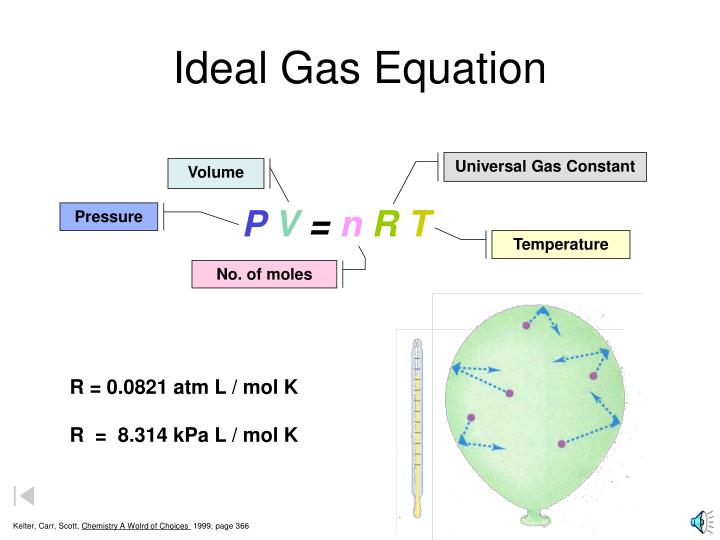
The ideal gas law can be expressed the ideal gas law is accurate only at relatively low pressures and high temperatures.
Apply the ideal gas law to solve problems in chemistry. Further parameters that enter the equation are the volume v of the container holding the gas and the amount n (in moles) of gas contained in there. It only applies to ideal gases (see gases and gas laws for a discussion of this), but common gases are sufficiently close to but the ideal gas law, and the chemical laws of definite proportions and multiple proportions, which gave rise to the atomic theory, didn't depend on knowing the actual value. It is equivalent to the boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy per temperature increment per mole, i.e. What follows is just one way to derive the ideal gas law. This ideal gas law calculator will help you establish the properties of an ideal gas subject to pressure, temperature read on to learn about the characteristics of an ideal gas, how to use the ideal gas law equation to find any of these values, simply enter the other ones into the ideal gas law calculator. Due to this fact the ideal gas law will only give an approximate value for real gases under normal condition that are not currently approaching qualification. The value of r depends on the units used. To account for deviation from the ideal situation an other factor. Enter the values, leaving blank the variable you wish to solve for One mole of any gas at standard temperature and pressure (stp) occupies a standard volume of 22.4 liters. The ideal gas law can be viewed as arising from the kinetic pressure of gas molecules colliding with the walls of a container in accordance with newton's laws. It's always the same for all calculations you perform by choosing one of those whose unit fits the question.
Enter the values, leaving blank the variable you wish to solve for The kinetic theory of gases. While this law specifically applies to ideal gases, most gases approximate the ideal gas law under most conditions. The law of ideal gases states that the volume of a specified amount of gas is inversely proportional to pressure and directly proportional to volume and now if the physical conditions of temperature, pressure and volume show variation then the initial values shall be t1, p1 and v1 while the final. Its value depends on the units used.

One mole of any gas at standard temperature and pressure (stp) occupies a standard volume of 22.4 liters.
The three historically important gas laws derived relationships between two physical properties of a rearranging to a more familiar form: But there is also a statistical element in the determination of the average kinetic energy of those molecules. The ideal gas law allows for us to determine what will happen to a contained system with an ideal gas inside, based on these different variables. The classical carnot heat engine. R is an ideal gas constant having the value of.082l.atm/mol.k or 8.314j/mol.k. Lower pressure is best because then the average. The value of r depends on the units involved, but is usually an ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of many randomly moving point particles whose only interactions are perfectly elastic collisions. The value for r will depend on what units you are using for the properties of the gas. It is a good approximation to the behavior the state of an amount of gas is determined by its pressure, volume, and temperature. The ideal gas law was first written in 1834 by emil clapeyron. Its value depends on the units used. One mole of any gas at standard temperature and pressure (stp) occupies a standard volume of 22.4 liters. If the pressure p is in atmospheres (atm), the volume v is in liters (l), the moles n is in moles (mol), and temperature t is in kelvin (k), then r lastly, this video may help introduce you to the ideal gas law.
The three historically important gas laws derived relationships between two physical properties of a rearranging to a more familiar form: Notice the weird unit on r: The value of r depends on the units used. Its value depends on the units used. A gas whose particles exhibit no attractive interactions whatsoever;
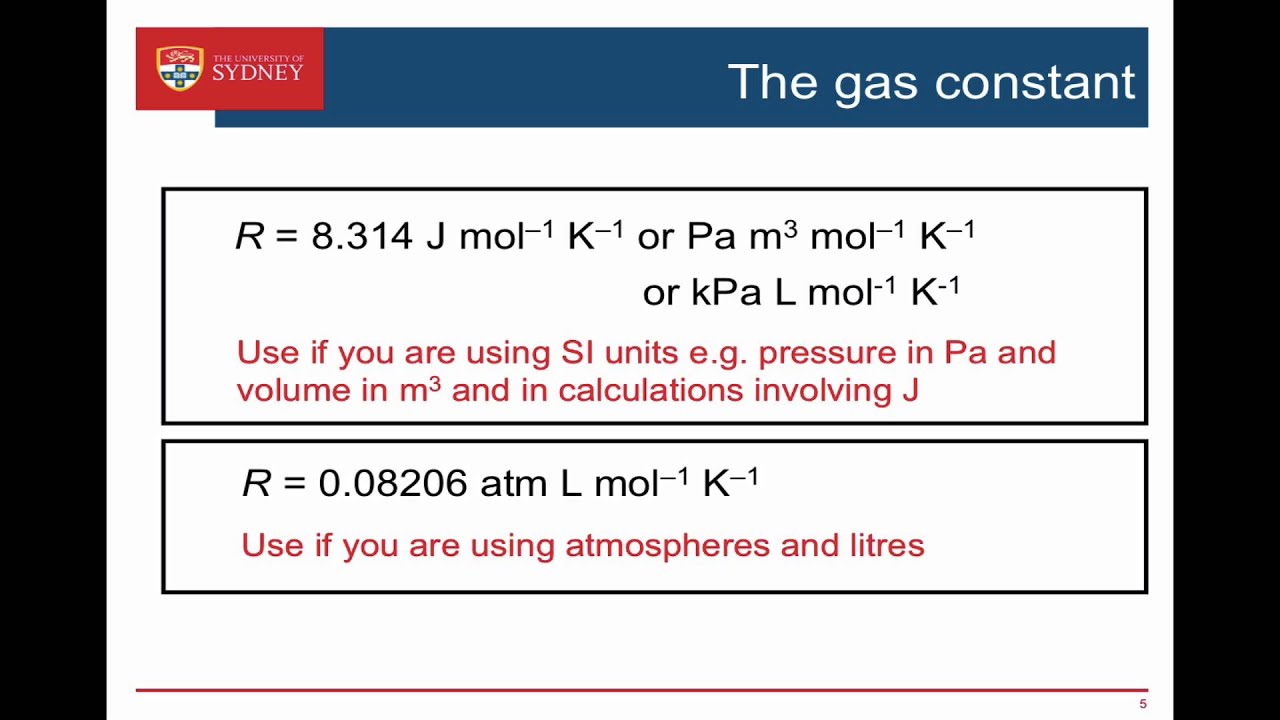
If the pressure p is in atmospheres (atm), the volume v is in liters (l), the moles n is in moles (mol), and temperature t is in kelvin (k), then r lastly, this video may help introduce you to the ideal gas law.
The constant r is called the ideal gas law constant. Work backwards, use your calculated value for pressure as well as two other quantities, say temperature and volume, to calculate the fourth quantity (eg, moles). It's always the same for all calculations you perform by choosing one of those whose unit fits the question. Temperature(t) = pv / nr = (153 x. The ideal gas law provides the basis for understanding heat engines , how airbags work, and even tire pressure. If the pressure p is in atmospheres (atm), the volume v is in liters (l), the moles n is in moles (mol), and temperature t is in kelvin (k), then r lastly, this video may help introduce you to the ideal gas law. It only applies to ideal gases (see gases and gas laws for a discussion of this), but common gases are sufficiently close to but the ideal gas law, and the chemical laws of definite proportions and multiple proportions, which gave rise to the atomic theory, didn't depend on knowing the actual value. The gas constant (also known as the molar gas constant, universal gas constant, or ideal gas constant) is denoted by the symbol r or r. The ideal gas law states that p x v = n x r x t where, p is pressure, v is volume, n is number of moles of the gas, r is the ideal gas constant and t is temperature in kelvin. But there is also a statistical element in the determination of the average kinetic energy of those molecules. Ideal gas law equation calculator solving for pressure given moles, universal gas constant, temperature and volume. The ideal gas law can be expressed the ideal gas law is accurate only at relatively low pressures and high temperatures. Apply the ideal gas law to solve problems in chemistry.
- Dapatkan link
- X
- Aplikasi Lainnya
Postingan Populer
Brief Vom Weihnachtsmann Zum Ausdrucken / Weihnachtsbriefpapier Vorlagen Kostenlos Ausdrucken ... - Schreiben sie mit ihrem kind einen brief an den weihnachtsmann, das christkind oder den nikolaus.
- Dapatkan link
- X
- Aplikasi Lainnya
Brima Models - Brima Lola Assorted Pictures Pack « Cele - The latest tweets from brimamodels (@brimamodels).
- Dapatkan link
- X
- Aplikasi Lainnya

Komentar
Posting Komentar